
The additional CPU load on top of the “real work” the device is doing increases based on the number of flows per second, and can consume a significant fraction of the CPU per a Cisco whitepaper (PDF). This can become a problem with high-speed devices where many conversations are concentrated onto a link. Device performance at high volumesĪs noted above, sFlow does minimal work on the network device, versus NetFlow which uses the device’s CPU and RAM to implement the flow cache. For detecting and drilling down to investigate security issues, this can be significant. The packets sampled may not reflect every flow (for instance, short bursts). However, sampling has the downside that there may be gaps in visibility. SFlow is thus more scalable than traditional NetFlow. If you’re not doing sampling, scalability becomes an issue. But as traffic volume mushrooms, it becomes less and less feasible to collect every flow. It’s easy to see per-host details, notice localized anomalies, and investigate particular flows. This granularity of NetFlow is attractive for examining traffic with an individual host. NetFlow aggregates data about all packets into flows locally at the device thus it can’t by happenstance miss a conversation by failing to sample the relevant packets. NetFlow’s partisans have long argued that NetFlow can be more accurate than sFlow. Here are the main differences between the two technologies. The differences between NetFlow and sFlowĪvi Freedman makes an apt analogy to monitoring vehicular traffic: “… while NetFlow can be described as observing traffic patterns (‘How many buses went from here to there?’), with sFlow you’re just taking snapshots of whatever cars or buses happen to be going by at that particular moment”.

#NTOPNG GRAFANA FREE#
#NTOPNG GRAFANA WINDOWS#
ManageEngine NetFlow Analyzer (FREE TRIAL) A traffic analyzer that installs on Windows Server and Linux and deploys the NetFlow, IPFIX, J-Flow, NetStream standards.SolarWinds NetFlow Traffic Analyzer EDITOR’S CHOICE The leading network traffic analyzer.Here’s our list of the best NetFlow analyzers & collectors: Its knowledge of the IP protocols enables it to interpret packets and work in terms of flows.
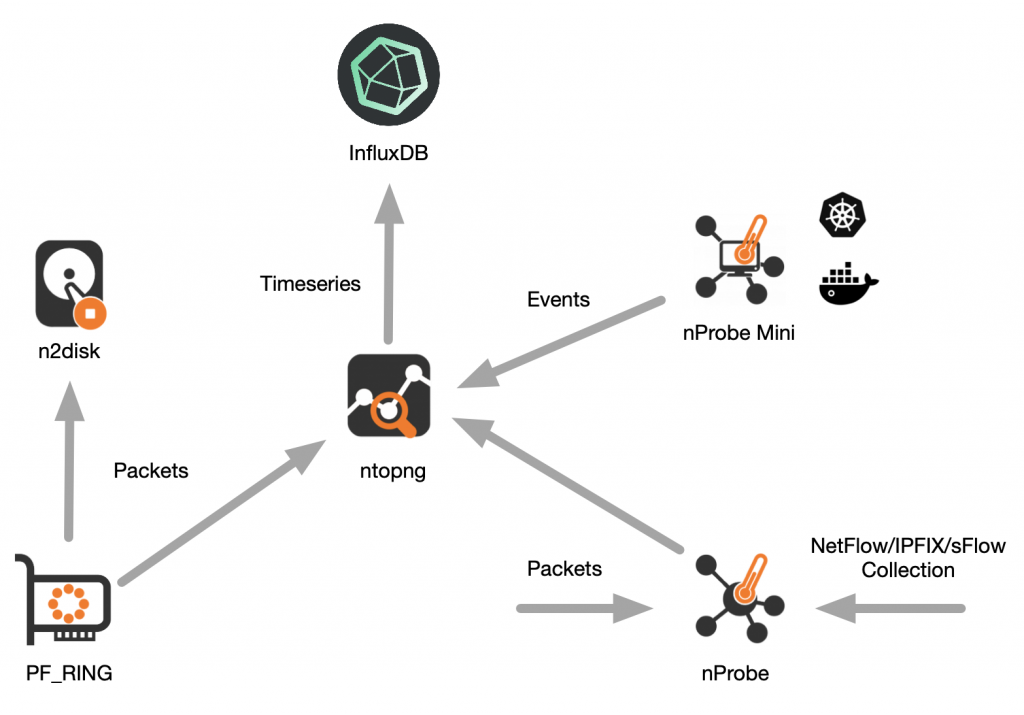
NetFlow thus only handles IP, focusing on OSI model Layers 3 and 4. NetFlow is stateful and works in terms of the abstraction called a flow: that is, a sequence of packets that constitutes a conversation between a source and a destination, analogous to a call or connection.Ī NetFlow exporter device collects data on the IP traffic entering/exiting the device it inspects packets and groups them into flows by inspecting particular fields: the source and destination addresses, protocols, ports, etc.ĭata on observed flows is rolled up from the packets and cached locally (in the flow cache), then it’s periodically exported to the collector based on active and inactive timeouts. NetFlow is a network protocol developed by Cisco that notes and reports on all IP conversations passing through an interface.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
